
Written by Amanda Gummer
20 years experience working with children and families
Two very hot topics at the moment but the approaches to increase diversity and improve inclusion can seem to conflict with each other, preventing either of them from being fully achieved. In order to achieve true diversity and inclusion we need to rethink some of the accepted wisdom.
When we talk about inclusion, we are often referring to disabilities and making sure children with additional needs are able to access the play or developmental opportunities that other children can. Similarly, when we talk about diversity, we’re usually talking about race, and occasionally gender. However, to truly be inclusive and diverse, we need to look outside of physical, and even mental conditions, and consider factors such as culture, geography, socio-economic status, and age. Only then can we achieve full inclusion and by breaking down those barriers we will automatically increase diversity. First, it is helpful to look at the evolution in our approach to inclusion. The same diagram can be used for diversity.
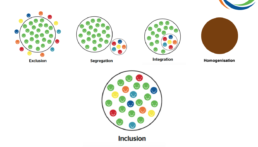
However, not everyone is on the same journey or going at the same speed on this. For example, many playgrounds were commissioned decades ago when the concept of inclusion wasn’t a priority – at best, there was a single, wheel-chair accessible piece of equipment – very little consideration was given to other disabilities and conditions which impact a child’s ability to play.
The toy industry has been stuck using the segregation approach for years – toys designed for children with additional needs are not readily available in mass-market toy shops or supermarkets and so are not able to benefit from the economies of scale of the most popular toy brands and are therefore more expensive and seen as very niche.
Clearly segregation is where the diversity movement started. Integration wasn’t much better for increasing racial tolerance and appreciating individual differences, but I think that the biggest backwards step was when, possibly with the best of intentions, we moved towards homogenisation. The principle being that if not everyone could have something, no one should. So everything became bland – we introduced a national curriculum which meant that children in a vibrant inner city school couldn’t make the most of the opportunities in their community because the kids in the rural village school didn’t have the same access, and children living in the countryside with access to lots of space and natural resources were not able to make the most of that in their education because it wasn’t accessible to the kids in the inner cities. Examples of this one-size-fits-all approach can be seen in lots of walks of life – from the rise in chain stores and the loss of individual towns’ personalities, to pre-packaging of food, fast fashion – the list goes on.
The result? An education system that is inflexible with very narrow definitions of success, playgrounds that are vandalised and misused because they’re not inclusive enough (not enough children are using them for them to be seen as a community asset and protected by the people in those communities), High Fat Salt and Sugar packaged foods, and a loss of character on our high streets. This all contributes to a lack of understanding and appreciation of individual differences and differing needs. And it is time for that to change.
I’m focussing on toys and play as that’s what I know but I’m fairly certain this is relevant in a lot of other arenas. We need to take some bold steps and recognise that true inclusion comes from appreciating children’s differences – and this naturally leads to more diversity. By considering all of the potential barriers to inclusion and working to remove them we are automatically increasing diversity. A playground that includes challenging risky play will not only appeal to children with ADHD but will also be used by older children and maybe those who can’t afford to go to the theme parks but crave a bit of an adrenaline rush. Understanding the dress codes of different cultures allows equipment to be included that doesn’t require climbing or leg lifting and is accessible to children in those clothes, as well as children on crutches.
So what’s to be done. Well first of all we need to get rid of the tokenism or ‘inclusion theatre’ all the things that look good and seem like they are promoting inclusion but are not based on any evidence and in the worst cases may actually be impeding inclusivity. To be truly inclusive and increase diversity, we need to take an evidence-based approach and include consultation with all stakeholders – whether that’s in town planning, toy design, playground procurement or shop layouts.
We also need to realise that a single product/brand/service can’t be all things to all people but should be accessible and relatable to by the people it’s designed for. A toy can not be multisensory and stimulating whilst also being quiet and relaxing. The important thing is to make sure that everyone’s needs are respected and catered for overall.
It’s really not rocket science but we need to update our approaches to both inclusion and diversity if we’re ever to really achieve either.
Amanda is a research psychologist and founder of the Good Play Guide: www.goodplayguide.com

