Committing to a queerer future in the university

Written by Alex Baird
they/them
Before moving to the Higher Educator sector seven years ago, I worked in various schools for over twelve years, latterly as Director of Sport. At the University of Bedfordshire I am a Senior Lecturer in Sport and Physical Education, an EDI Lead, and the Vice Chair of the LGBTQ+ Alliance staff network. I have just finished an EdD at UCL and the research I write about here constituted my EdD thesis.
In the process of moving from teaching in schools to lecturing in Higher Education (HE) and then embarking on a doctorate, I have been encouraged to read, reflect, and write more. I have gravitated towards my LGBTQ+ lived experiences and perspectives and I find myself increasingly motivated to carry out LGBTQ+ themed research. Being a LGBTQ+ researcher encompasses treading a different and uncertain path. In anticipating a few negative reactions to my research or worse still not being heard at all, I will attempt to speak calmly and clearly in order to bridge a connection and appeal to the shared interests that we might have between us.
LGBTQ+ leadership has often been excluded from UK HE, HE leadership research and wider leadership research, meaning leadership is narrowly understood (Lumby & Moorosi, 2022; Thomson, 2017). The individualistic, fixed, and binary conceptualisations of leadership, also enable and maintain prevailing power structures and inequalities (Ferry, 2017). For this reason, I was excited to hear about a proposed LGBTQ+ leadership development programme within the specific context and current climate of UK HE and further still when I was given access as a researcher to query leadership and leadership development.
The LGBT Leadership Development Programme I attended was delivered within one post-92 university and consisted of three formalised classroom days and individual mentorship. I had not anticipated, since I was not employed at the host university, being a participant as well as observer on programme days. However as soon as I arrived on day one, attendees drew me into the group and session activities. I tried to extend a reciprocal level of openness about my personal and professional experiences while balancing my role of observer, being interested without becoming too active. I learnt to wait a while and let other attendees ask a question before I did. I was invited to attend five further socials and three LGBTQ+ network events which brought me even closer to attendees’ lives. Attendees willingly engaged in interviews and I became aware of how their voices were entangled with other voices, the atmosphere of the programme’s queer space, their perceptions of the wider university, and their loyalty to the programme and its survival.
The energy, lightness, and freedom of the programme’s queer space produced new ways of thinking about, seeing, and enacting leadership. The community of LGBTQ+ attendees who came together (which included both academic and professional staff) facilitated intergenerational queer knowledge sharing amongst LGBTQ+ staff and offers an example of how distributed leadership and discussion works in practice. LGBTQ+ leadership was conceptualised as listening to, valuing, and developing people, and challenging inequalities by voicing an alternative perspective. A form of leadership which is relational, collective, creative, temporal, and offers some resistance to the negative pressures of neoliberalism. Enacting LGBTQ+ leadership was seen as being different (at times) from management rather than the two being interchangeable terms; attendees sheltered their team from or utilised market forces in UK HE to support inclusion and recognised that leadership did not necessarily require an authority role.
I know of three attendees who were promoted during or shortly after attending the programme however this overlooks the longitudinal, curvilinear, and wider outcomes for both attendees (mental wellbeing, career satisfaction, and career direction) and the organisation (development and retention of diverse talent). Instead of assimilating or conforming to normative versions of leadership, LGBTQ+ lives were attached to leadership with growing pride and joy. Crucially, though, the attendees in this queer space reflected upon and redefined the meaning given to authenticity (Fine, 2017), which was viewed by some attendees as beyond an ‘outness’ (recognising the nuances involved in this act), rather knowing oneself (an ongoing process) and embracing this. Whilst Authentic Leadership Theory (Avolio et al., 2004) fails to consider the complexities of relational and contextual factors, the attachment of this concept to the LGBTQ+ leadership development programme offered personal benefits to LGBTQ+ attendees’ wellbeing and leadership potential (Fletcher et al., 2024) and encouraged qualities in their leadership, which have been identified as being essential to UK HE (Spendlove, 2007; Bryman & Lilley, 2009).
The programme and LGBTQ+ mentorship readdressed feelings of powerlessness in the wider university, and nurtured and developed LGBTQ+ staff talent (and the university’s emerging leadership). This included mentors offering support when mentees applied for specific jobs during the programme’s duration and mentors explaining pathways for academic staff (which for some had been previously obstructed); clarifying the university’s systems and structures; and advising mentees to network with colleagues within HE. Attendees gained confidence to walk their own paths and voice alternative viewpoints. Attendees also spoke about the ‘softer’ merits of the programme, for example friendships continuing to blossom. Attendees viewed leadership development as a continual process of learning from and reflecting upon their leadership and life experience. It was also noted that progression was not always available, nor should it be the only aspiration, given the risk and limitation involved.
In sharing these findings to stimulate future versions of LGBTQ+ leadership development programmes I have been asked why a LGBTQ+ leadership development programme should be prioritised over other protected minority groups. I am not suggesting that LGBTQ+ staff have a superior need to others rather that this research indicates there is a value to leadership development programmes which have a specific focus and membership. However a LGBTQ+ leadership development programme would be particularly meaningful at this moment in time, when LGBTQ+ staff and students may be feeling less safe given the backdrop of a ‘culture war’ in the UK and a global ‘moral panic’ surrounding trans people. HE should be at the forefront of leading the way to positive societal change. I hope my research makes a valuable contribution to guiding future LGBTQ+ leadership development programmes and their accompanying research.
References
Avolio, B. J., Gardner, W. L., Walumbwa, F. O., Luthans, F. & May, D. R. (2004) ‘Unlocking the mask: A look at the process by which authentic leaders impact follower attitudes and behaviors.’ The Leadership Quarterly, 15, 801-823.
Bryman, A. & Lilley, S. (2009) ‘Leadership Researchers on Leadership in Higher Education.’ Leadership, 5(3), 331-346.
Ferry, N. C. (2018) ‘It’s a family business!: Leadership tests as technologies of heteronormativity.’ Leadership, 14(6), 603-621.
Fine, L. E. (2017) ‘Gender and Sexual Minorities’ Practice and Embodiment of Authentic Leadership: Challenges and Opportunities.’ Advances in Developing Human Resources, 19(4), 378–392.
Fletcher, L., Pichler, S. & Chandrasekaran, L. (2024) ‘Songs of the self: the importance of authentic leadership and core self-evaluations for LGBT managers.’ Journal of Managerial Psychology, 39(2), 131-145.
Lumby, J. & Moorosi, P. (2022) ‘Leadership for equality in education: 50 years marching forward or marching on the spot?’ Educational Management Administration & Leadership, 50(2), 233-251.
Spendlove, M. (2007) ‘Competencies for Effective Leadership in Higher Education.’ International Journal of Educational Management, 21(5), 407–417.
Thomson, P. (2017) ‘A little more madness in our methods? A snapshot of how the educational leadership, management and administration field conducts research.’ Journal of Educational Administration and History, 49(3), 215-230.
#AllTheThings

Written by Helena Marsh
Helena is a WomenEd co-founder, mum of three and experienced school and Trust leader. In her ninth year of secondary headship, Helena has also held the role of MAT CEO. An advocate of flexible working, Helena co-wrote the ‘Flexing our Schools’ chapter in the first WomenEd book and has been an active supporter of the Flexible Working Ambassador Scheme and the MTPT Project.
Spending the day among some incredible inspiring women at the ‘Breaking the Mould’ event on 9th March at Milton Road Primary School, Cambridge, was a fabulous way to mark this year’s International Women’s Day.
Hannah asked me to contribute to the event when we met for an after work mocktail in May 2023. At the time, having this little spot of feminist joy to look forward to on the horizon really uplifted me at a particularly bleak moment in my leadership career.
Several months later, I was not disappointed. Featuring amongst a programme of kick-ass women gave me a real sense of personal and professional rejuvenation.
My session, entitled ‘What’s the point of cake if you can’t eat it?’, focused on my experiences, as a mum of three, of gendered perceptions of leadership. In my 15 years as a senior leader, I’ve been conscious of women stepping away from the profession, and their leadership potential, citing selfishness and a pragmatic need to focus on their families, as the reason.
To coin a phrase by Summer Turner, I questioned: ‘Are the boys also worrying about this?’ Do men perceive becoming a dad and maintaining their career as ‘having it all’?
Gender pay gap research reveals that they don’t. The Fatherhood Bonus, in stark contrast to the Motherhood Penalty, rewards men for becoming fathers. While women are stepping down or away to focus on caregiving and accepting the inevitability of this pause/permanent freeze in their professional journey, men are, statistically, enjoying promotion and pay progression when starting a family.
My presentation focused on the factors, institutional, societal and personal, that lead to women feeling as though progressing professionally is not a viable choice once becoming a mum. I concluded that wholesale changes to sector expectations of leaders is necessary. As Jill Berry wisely observes, if having a job and a life isn’t achievable, there’s a problem with the job.
The other inputs to the day complemented this theme. Particularly Niamh Sweeney’s rousing cry to tackle the injustices within the profession that inhibit and preclude. Niamh’s anecdote from her recent trip to the States chimed with many of us in the audience. The audacious goal of winning ‘all the things’ spoke to a refreshing cultural ambition. Meanwhile, many of the other talks highlighted the importance of acknowledging feminine leadership traits and valuing the benefits of diversity in leadership teams.
I left the day reflecting on how often ‘having it all’ is misunderstood for ‘doing it all’. My Mother’s Day stash of gifts that I received the following day from my little ones included various iterations of listing pads. As a fan of organisational stationery, I was chuffed with my haul. However, it did make me recognise how much of my sense of success as a mum and leader is measured through my accomplishment of ‘stuff’. Many women that I have worked with pride themselves on getting all the sh*t done and to an exceptional standard, often at the expense of their personal health and wellbeing.
As I acknowledged in my IWD talk, the weight of the mental load that mums carry, let alone mum leaders carry, is immense. It’s important that having #AllTheThings doesn’t necessitate us doing everything but having our fair share of whatever it is we strive for, whether that’s cake, career development opportunities or childcare responsibilities.
Reflecting on Privilege and Pupil Premium

Written by Gemma Hargraves
Gemma Hargraves is a Deputy Headteacher responsible for Safeguarding, Inclusion and Wellbeing.
I recently attended a national Pupil Premium Conference in Birmingham. The first speaker asked for people to raise their hands if they have personally experienced poverty – I have not, so I did not raise my hand. The number of people who did was striking. I was reminded of my experience at Bukky Yusuf’s session at the first Diverse Educators conference when we were asked how many boxes we tick in terms of diversity. I am very aware of my luck, my privilege, and whilst my father would have proudly proclaimed his working class roots he made sure I had a comfortable upbringing never wanted for anything.
Spending the day surrounded by educators who care deeply about supporting students and families eligible for Pupil Premium I was struck by the need to get to know these students at my school better. Since joining the school in September I know some very well, for various reasons, but others I have not met yet. Sean Harris’s keynote was compelling about rewriting the story of disadvantage in schools and communities.
We cannot assume all students in receipt of Pupil Premium funding face the same challenges. When I say “we” I mean myself, as Deputy Headteacher in charge of Pupil Premium strategy, but all teachers and staff in schools. Vital here are Form Tutors who see the students every morning and offer a caring and consistent welcome. Also, Receptionists, canteen staff, all teachers and leaders in schools. “We” here should also mean policy makers – those who decide who qualifies for Pupil Premium, and Service Pupil Premium, and who doesn’t but who also need to be supported (of course this is all students but I am especially thinking of those who are only just above the Pupil Premium qualifying line, disadvantaged sixth formers, of young careers, of others with additional needs). We must all endeavour to know these pupils as individuals and to give them opportunities to shine.
There are practical and logistical challenges of course. Schools Week this week reported that school will have to wait until May to find out their pupil premium funding allocations for 2024-25. The data was supposed to be out in March but had been hit by a ‘problem’ with identifying eligible reception pupils. This clearly makes it more challenging for schools to budget and perhaps recruit but we just not lose sight of the children affected. Similarly, when focusing on outcomes, Progress 8 or some other measure we must remember there are individual students and families behind these numbers.
Of course, our approach must be intersectional. A child is not only “Pupil Premium” they may also be a devout Muslim, disabled, a child of LGBT+ parents or indeed all or none of these but we will only know and be able to celebrate this if we get to know the pupils and families better. We must find funds to support them in ways they need, not what we assume will be generically helpful.
And while literacy is of course important and key to probably every Pupil Premium strategy, and improving educational outcomes can be transformative, we must also focus on cultivating a sense of belonging, confidence and joy. I’ve been doing a lot of work on inclusion, diversity and belonging in schools over the past few years, but this conference gave me a renewed focus on poverty and inequality. In the spirit of pledges from previous WomenEd and DiverseEd events, I am now committing to spend more time reading, thinking, and researching about poverty and inequality in my community but also, of course, getting to know the students and families so they can truly flourish.
Diversifying Coaching in Education – A Funded Opportunity for the #DiverseEd Community to Train to Coach

Written by Yasmin Ariff
Yasmin Ariff is a Partner and Director of Education at the CVP Group. CVP Group specialise in professional coaching training for managers and business leaders. They create coaching cultures across UK organisations, supported by the National Apprenticeship Service.
I wish I’d found coaching earlier in my teaching career. It has made me a better person on so many levels. But it came at a cost. Having invested £8000 of my own money into coaching training, it’s fair to say, although it’s been worth it, it also broke the bank balance.
It made we wonder whether coaching would ever be a truly diverse and inclusive profession when only those with a higher-than-average income could afford the training. Even hiring a coach can cost around £100 per hour.
So, how can we, as leaders, democratise coaching in Education?
How can we create a pool of coaches that represent the diverse backgrounds of our Educators?
If only there was a government-funded training programme for aspiring coaches that removed the barrier of cost…
If only there was a coaching training programme that promoted and included a range of diverse educators…
Look no further!
CVP Group and #DiverseEd are partnering to deliver a funded training programme in October 2024 for aspiring coaches in England.
To apply, you will need to complete this #DiverseEd EOI and they will then send you the CVP ROI with the #DiverseEd Referral Code.
Introducing the Level 5 Coaching Professional Apprenticeship
Our unique approach supporting aspiring and existing diverse leaders will support you to:
- engage with your workforce
- promote active listening skills
- deepen your understanding of what motivates teams
- improve staff retention
- support other aspiring or existing diverse leaders
The 12 month apprenticeship programme is delivered online including an End Point Assessment.
The Level 5 Coaching Professional Apprenticeship enables learners to work towards a nationally recognised qualification that meets coaching professional body standards (ICF, EMCC and Association of Coaching). The coaching professional standard has been created by leading organisations with existing coaching cultures and expertise in leadership.

Figure 1. Organisations who created the coaching standard
In a group dedicated solely to Diverse Educators, you will cover coaching disciplines such as:
- how to plan and structure coaching sessions;
- cognitive behaviour techniques to reframe limiting beliefs;
- principles of neurolinguistic programming;
- schools of psychology such as Carl Rogers, Gestalt and Freud;
- leadership theory and change management;
- managing and celebrating diversity in your coaching practice;
- ethics and professional codes of conduct for coaches as well as how to demonstrate return on investment to stakeholders.
Over 12 months you will be provided with the tools you need to create a coaching model tailored to organisational needs.
Our #DiverseEd cohort will also have the unique opportunity to attend additional #DiverseEd sessions with Hannah Wilson to explore diversity, equity and inclusion in coaching further.
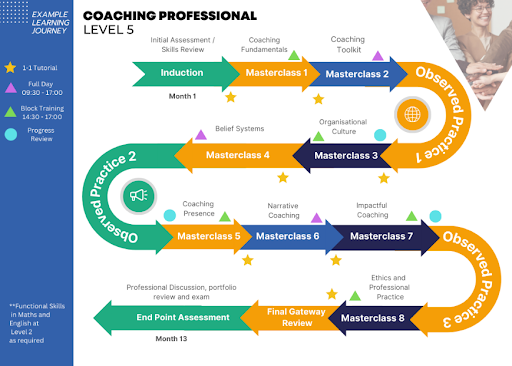
Figure 2. The Coaching Learning Journey
The apprenticeship requires the application of coaching skills in the workplace which will be tailored to fit into your day-to-day job role. Coaching apprentices will receive wrap around support throughout the year so they can apply their coaching skills in the workplace. Many of our current apprentices are using their coaching skills to develop different aspects of education such as:
- teaching and learning
- behaviour and attitudes
- well-being and leadership.
Ongoing careers guidance and support for apprentices includes attending a range of webinars delivered by expert coaches which demonstrate how your coaching skills support career advancement. In addition, there will be plenty of opportunities to develop personally through CVP’s well-being events, an online community and learning forum as well as your bespoke personal development plan, including an opportunity to win our Easter fitness hamper with CVP’s annual spring into fitness competition.
The #DiverseEd Coaching Community
We are building a #DiverseEd coaching community which will be the first of its kind.
We know the current coaching landscape in Education is not representative of the leaders it serves so we want to upskill educators as coaches in our community to empower each other.
CVP Coaching apprentices will be the first to pilot a funded coaching programme for the #DiverseEd community, where CVP coaching apprentices will have an opportunity to join the #DiverseEd Coaching directory.
The inaugural cohort will run October 2024 and we anticipate that places will be in high demand.
What Attendees are Saying About Us
Here’s what our current trainee coaches have to say about the programme:
“This course has been the perfect opportunity to keep learning and development at the heart of what I’m doing. It’s extremely well organised and resourced. Yasmin’s care, expertise and passion ensures we as the participants are motivated and supported every step of the way.”
Claire, Senior Leader Education.
“Great session, the demonstration where we got to see it in action was really powerful to have that practical example. It is about simple steps being done well. You have to learn the art (which can be complex) and then not let it cloud your basic best practice.”
Apprentice, Masterclass 2.
“The level 5 professional coaching course was thoroughly enjoyable and purposeful. I refined skills that were instantly transferable to the workplace but also deepened my reflective practice to understand how my own principles surface at work. I felt fully prepared going into to EPA and confident enough to show off my portfolio. Lots of elements in the portfolio I still use in my coaching sessions today. The course complemented full-time employment in education and didn’t seem too laborious as all the tasks seemed purposeful.”
Rosie, Assistant Headteacher
Join Us in October 2024!
To be eligible for funding you must meet the following criteria:
- Work 16 hours or more per week;
- Have lived in the UK / EU for 3 years or more prior to enrolment;
- Spend over 50% of your working week in England;
- Have a contract of employment.
Are you interested but not in employment? Do you live outside England? We are pleased to open this programme to diverse leaders beyond England on a self-funded basis. If you would like to have a conversation with one of the team at CVP Group to find out more, reach out to sarah@cvpgroup.co.uk
What Next?
Whether you have made your mind up or would just like to find out more about the course content, please complete the Register of Interest Form that #DiverseEd will send you and our coaching engagement team will contact you to set up a meeting.
I will be delivering a large part of the programme. With over 20 years’ experience in schools, I am looking forward to reconnecting with leaders to create powerful coaching cultures in schools.
To find out more about my own journey as a leader in education, visit my website here.
Leaving a Legacy: Saying Goodbye to My Shero – Karen Giles

Written by Hannah Wilson
Founder of Diverse Educators
There was a flurry of activity on my social media timeline yesterday following the devastating news that we have lost the beautiful soul that is Karen Giles. The outpouring of love is not a surprise as Karen is a well-known, well-respected and well-loved educational leader. We had been expecting the news for a while as she had been really unwell for a long time, but it is still a shock to realise that she has gone forever.
I had received an early morning text from a mutual friend and spent most of the day crying as different people reached out with personal messages to share their pain of losing our dear friend. I did not know if it was public knowledge so I did not share anything on my socials – just in case people who knew her had not heard the sad news, and to respect the family’s privacy at this difficult time, but by the evening I realised others had shared the news and the ripples of shock had widened. I thought about her and her impact on me all day and went to bed penning a piece to capture the essence of what a special human being she is (struggling to write her in the past tense).
Karen was and will continue to be the epitome of everything I believe in when it comes to leadership: she lives and models her values; she practices what she preaches; she is authentic; she has integrity; she is humble; she serves her community; she advocates for others; she has impact. Above all she has a huge heart, she is very kind and she nurtures everyone around her. She has a very special gift of making you feel like the only person in the room – totally seen, totally heard, totally understood and totally supported. Anyone in her orbit is lucky to sponge up a little bit of her presence. I think we all need to be a bit more Karen Giles.
I met Karen multiple times in a short period of time nearly a decade ago: we were both school leaders in London; we were both committed to empowering women leaders – she attended and supported #WomenEd events; we both contributed sessions to the Leading Women’s Alliance events; and as I started my NPQH she was one of the facilitators on our residentials with Ambition School Leadership. Every time I crossed paths with Karen I fell a little more in love with her. I don’t put many people on a pedestal but Karen was up there – she was one of my ‘wise women’ who became not only a guide but a friend. She relentlessly cheered on, championed and sponsored people around her. I am very lucky and very grateful to have been able to stand in her light and feel the warmth of her soul.
Every time I needed Karen she was there for me, and I know she was there for everyone else in her multiple circles too. She supported me out of a tricky Deputy Headship into Headship, she supported me out of my Headship and into my independent work. She held a mirror up to me to consider my future and helped me realign my Ikigai. I can remember visiting her at her school one morning following a breakfast meeting and she said to me: “Hannah Wilson, where ever you have been, whatever you have been doing, this is your calling”. I supported her through a relationship breakdown and into an Executive role; I supported her in considering her options post-retirement. I was excited at her becoming a coach, finding a home in Barbados and training to be a celebrant. We joked that if I ever got married she would host the ceremony for us. I told her she had multiple books in her and I think she had started a few of them.
We called each other for professional favours and the answer was always a Yes, no matter what it was/ when it was. She contributed to our #DiverseGovernance series during lockdown and she was one of our keynotes at our #DiverseEd event post lockdown. Lots of the posts on X reference how inspiring she was and comment on how she modelled inclusive, servant leadership. I spoke at a few leadership events at her school and spent some time with her associate headteachers. Karen was an introvert and a quiet leader but she had an enormous, yet gentle, presence, she hustled me into many an event that I was not on the guest list for with a smile and a polite request!
‘Yes’ was a word we had bonded over at LWA. I had a run a session at LWA on The Power of Saying Yes inspired by the book by Shonda Rhimes, about grabbing opportunities with both hands. She had made a deal with me, there and then, that if she said yes more could I say a few more nos. As we negotiated there was a twinkle in her eyes – we were total opposites in so many ways but had so much in common when it came to the important stuff. I really valued the mutual respect, mutual trust and mutual love we held for each other.
When we were writing the first #WomenEd book, 10% Braver, each chapter author chose a role model to amplify and showcase. Karen was my natural choice. At the end of chapter 1 this is what I wrote about her:
“Role Model: Karen Giles
Values-led leaders demonstrate that you can be a leader with a soul. Karen Giles is an Executive Primary Headteacher in London and a facilitator for Ambition School Leadership. I remember meeting her at one of my first NPQH sessions where she invited 64 aspiring headteachers to go for a leisurely jog around the conference room. She was immaculately dressed in a purple shift dress, matching tailored jacket and heels and gracefully leapt like a gazelle. I fell a little bit in love with her on the spot.
I was delighted Karen came to my session on The Power of Networking at the second Leading Women’s Alliance event. She is an old school networker and I am a new one, and we had a passionate discussion about Shonda Rhimes’ book ‘Year of Yes’. We both agreed that whilst ‘Yes’ is an enabler, women also need to be empowered to say ‘No!’
Karen has local, regional, national and global impact as a leader. She has taught and led in London schools for twenty-eight years and is currently a Local Authority School Effectiveness Lead Professional, working with leaders in sixteen schools. Karen has been a Leadership Coach since 2012, leading and facilitating a variety of mixed phase coaching groups and workshops as well as working with both Primary and Secondary participants. She served as an Ofsted Inspector from 2010-15, has been appointed as a Coach for the pan-London GLA Getting Ahead programme and is Primary Director for the London Leadership Strategy. She was the winner of the London Region National Teacher Award for Enterprise and Innovation in 2009 and serves as an advisory board member for the Varkey Foundation. Karen currently serves as Headteacher, a position she has held for thirteen years”.
I didn’t tell Karen I was writing about her, but I sent her a copy of the book with a post-it in it and a card when it was published. I know she was really touched and ever the humble person she was shocked I had chosen to spotlight her. Throughout her illness I have regularly sent her WhatsApp messages and voice notes to update her on the things we would normally discuss. I also sent her Mum a copy of the book so that her family could read it and play it back to her so she could hear the impact she has had on so many.
Leaving London our in-person catch ups happened less frequently, but whenever we could squeeze in a lunch or a brunch we did. I often drove down to her flat and she would spoil me rotten, and if we met somewhere central she would often arrive giggling that I had made her come out to the sticks to see the cows and the mud. Those who know Karen will remember her for resembling a Hollywood actress as she climbed out of her nippy sports car in a glamorous faux-fur coat.
One of the last times I saw her in person I took her out for a belated lunch to celebrate her 60th birthday. She was so full of life and excited for what the future held for her. It seems so unfair at the timing of her illness, as she stood on the cusp of her 3rd quarter.
Preparing for her next chapter in life and her career she asked me to run a session for her and some of her friends on how to leverage LinkedIn to grow their network/ profile. Not that she needed help with either as Karen was a brilliant connector. This is my LinkedIn testimonial for her:
“I can still remember the first time I met Karen Giles, she glided into the NPQH room and captivated 64 aspiring Headteachers. I have had a professional crush on her ever since! If you have read the #WomenEd book 10% Braver, I wrote chapter 1 and Karen is my role model at the end of it. Making a big impression on me as a senior leader and aspiring Headteacher, Karen became my unofficial mentor and my critical friend (she didn’t have much choice in the matter!) I had coaching as a Deputy Headteacher, a Headteacher and as an Executive Headteacher but it was often Karen I would turn to in a crisis to tap into her calm wisdom. She has supported me through pivotal decisions in both my professional and personal leadership journey. I have learnt lots from her, but we have also become friends through it all. I have heard Karen speak on numerous occasions – for Ambition School Leadership, for the Leading Women’s Alliance and for Diverse Educators – what always shines through is her integrity, her resilience and her quiet determination to do the right thing by her people (her pupils/ her staff/ her community/ her network). She is a brilliant role model, a supportive mentor, a transformational coach and an inspiring leader. If you have not connected with her, then what are you waiting for? Witness her fabulousness for yourselves”.
As you read the posts of Facebook, X and LinkedIn about Karen you will really capture the essence of her character, and will be able to appreciate the impact she had on so many people. Serving her community as the Headteacher of Barham Primary School for 20+ years she leaves behind her a huge legacy. More than that she was a global thought leader advocating for the rights of children around the world to have a good education.
To remember her, I was going to send something to plant in the school garden and some books to continue her commitment to diverse representation to the school but I have instead decided to create a Just Giving Page for her. The school can then work with her family on how to memorialise her. I love the idea of creating a school peace garden, or a mural, in her name if we can raise enough funds.
Find out more and donate to our fundraiser HERE.
Dearest Karen – you epitomised sisterhood and female solidarity. I am blessed to have met you and to have had you in my life as a mentor and a friend. Go join your loved ones and be an angel looking over us all. Thank you for everything you have done for us all. You will always be my Shero. All my love, Hannah xx
Open doors, Unequivocal mirrors, Pellucid windows

Written by Utha Vallade
Monday to Friday, Utha is an Associate Assistant Principal, leading on Raising Standards, Assessment and Reporting in an inner London secondary school. On Saturdays, she works as the co-headteacher of an all-through Saturday supplementary school. Passionate about supporting other educators on their leadership journey, in her not so spare time, Utha contributes to Step Up Network and leads on Partnerships, Diversity, Equality. Inclusion and Belonging.
As a dedicated senior leader working in a comprehensive, inner London secondary school, my journey in leadership has been defined by a commitment to continuous personal growth and professional development. Recently, I had the unique opportunity to shadow a headteacher working in a different school setting. My objective was to immerse myself in the daily responsibilities and challenges of leading a school and this experience offered me invaluable insights into the complexities and rewards of headship.
From the outset, I was fully welcomed into the smaller, rural school. The warmth and hospitality extended to me were a testament to the nurturing culture fostered by the headteacher. Throughout the week, I eagerly absorbed every leadership lesson and insight, recognising that the school’s environment and culture mirrored its authentic leadership.
What struck me most was the genuine care and respect evident in every interaction between teachers and students. Empowerment permeated the atmosphere, with students demonstrating remarkable personal growth and development under the guidance of supportive educators. Similarly, teachers and middle leaders flourished rapidly in their respective areas of responsibility and beyond. Witnessing these examples of student empowerment and staff development reaffirmed my belief in the transformative power of effective school leadership.
A key takeaway from this experience was the importance of being unapologetically caring and ambitious for all members of the school community. Every interaction, whether with students or staff, should be guided by a genuine desire to support and uplift others in the pursuit of academic outcomes and personal growth. The school I shadowed exemplified this ethos effortlessly, with caring and respecting others ingrained in its culture.
What impressed me the most was that this culture of care and respect was internalised by the school community. It was evident in the way students looked out for one another and how staff went above and beyond to support their students’ growth and well-being.
Moreover, the involvement of parents in the school’s daily life was inspiring. I saw examples of parents coming together to rebuild a fence to allow the play area around the pond to meet health and safety criteria. Another parent spearheaded a world-wide courageous advocacy programme which led students to bring conflict resolution and economic solutions to the local and wider school community. Whether rebuilding a fence or spearheading global advocacy programs, parents undoubtedly played a vital role in enhancing the school community. As an aspiring headteacher, I relish the opportunity to create an environment where everyone can flourish and thrive and for the students under my care to have a positive impact on our local and wider community. Therefore, witnessing these examples reinforced my commitment to foster positive impact in my school.
While the school environment was incredibly welcoming and nurturing, it was not without its challenges: uniform infringements, behaviour referrals and parental disagreements were part of daily school life which I have also observed in other educational settings. However, to me, the most striking difference was the timing of detentions and extracurricular activities. Due to its location in a rural town and its size (around 500 students), a significant number of students travelled to the school via coach. This meant that the school day revolved around the coaches’ departure times. As a result, detentions and clubs, including rehearsals for the school production or student-led assemblies had to run at lunch time rather than after school like in most London schools. All these challenges simply reminded me that the role of a headteacher carries immense responsibility and requires equally immense resilience and tremendous adaptability to the specific context of the school.
In conclusion, my week shadowing a headteacher was an insightful experience that reaffirmed my commitment to headship. It underscored the profound impact a caring and ambitious leader can have on a school community. As I continue my leadership journey, I will apply the lessons learned and strive to continue to make a meaningful difference in the lives of students and teachers alike.
ADHD Heads: How can we utilise neurodiversity in shaping the future of schools?

Written by Nadia Hewstone
Nadia is a certified executive school leadership coach. She left headship to start Destino Coaching and now supports school leaders with their own development as well as development of their teams.
Below is what I shared at the ‘Breaking the Mould 2’ in Cambridge for #IWD2024. I would love to hear from you with your thoughts and reflections on the themes I explore:
I am Nadia, founder of Destino Coaching – an organisation that supports Headteachers to remain strategic while tackling the enormous amount of operational challenges in schools.
I want headteachers to increase their influence over policy.
Usually, I’m invited to speak about ways to stay on track with your big goals in headship. Over many years I have developed several planning strategies to help me stay focussed and on track. The main principles are now tools I teach the headteachers I work with.
Looking back over my career I see that I became hyper focussed on finding ways to overcome the challenges I faced associated with being neurodivergent. This is what I want to explore with you today.
Over the next 10 minutes, I want to make a case for the need for neurodivergent leaders in schools as one of the key ways we will address the multiple systemwide issues schools are now facing.
- My story
Like many parents of neurodivergent children, I started to look at some of my own behaviours through the lens of my developing understanding of autism and ADHD about 10 years ago, when I was a headteacher. Both of my children have autism and ADHD and my own assessment of ADHD raised a question about potential ASD too – I have yet to find the time and space to investigate this but I have ADHD and while I am just one person with ADHD, I have now worked with many neurodivergent headteachers and have thought long and hard about what we bring to schools as a group.
As a woman with ADHD I face several struggles and I also experience a freedom I believe is unique to neurodivergent women. Here are some things about me that can appear strange to others:
- I stand up for meetings or regularly leave my seat if I am required to be seated.
- I often put tasks off until the last minute
- I find it difficult to follow people when they give long explanations or instructions. I can appear to be bored – and often I am!
- I have to try very hard not to finish other people’s sentences and speak over them in an attempt to speed them up
- I have to work extremely hard at relaxing and being calm – even though I know it is essential to my well-being
- I need others around me to attend to details as I find detail painfully difficult and race forward
- I break rules – especially when they don’t make sense to me
- I do not proofread my documents
The first time I went on a road trip with my deputy Steff, we stopped at a service station and her standout memory of this day was me getting out of the car before she’d finished parking. She still laughs at this memory now. While I see the funny side I also stand by the decision to do this – she is a stickler for doing things correctly, accurately, by the book – I am not. I saw an opportunity to get our Starbucks order in while she finished her perfect bay parking exercise – therefore cutting down lost time.
Steff and I were a match made in heaven! She was accepting of my pace and challenging about my shortcomings – she gave me space to lead my way and facilitated my growth through her attention to detail. I will love her for this forever.
Now that I recognise many of my behaviours as part of my ADHD, I am learning to work with them, quieten my inner critic and communicate more effectively so that others do not take offense.
As a headteacher, I implemented change very quickly and my high energy meant I took my team with me – they told me I was full of purpose and great fun to work with. I also disregarded things I saw as unnecessary restrictions. This was sometimes significantly risky but meant we cut through challenges and achieved things more quickly.
I’ll leave it up to you to imagine the downsides of all this for my school business manager!
I have had 12 female coaching clients over the past 5 years who have a diagnosis of ADHD and all of them report frustration with the restrictions placed on them by the education system.
Neurotypical heads undoubtedly experience this too – the difference is that people with ADHD view this as intensely impossible to work around.
Coaching women with ADHD is generally focussed on how to achieve their massive, exciting, propositus goals despite external barriers such as Ofsted, the National Curriculum and prescriptive working practices. Mostly they are successful once we work out how to embrace the difference.
People with ADHD are 60% more likely to be dismissed from a job, and three times more likely to quit a job impulsively (Barkley, 2008). This is a great loss to society and I hope we can reverse this in schools so that we can secure a way forward that serves young people.
2. Broken system – needs radical change
If you work in a school, I don’t need to tell you the system is broken:
- A widening gap between rich and poor educational outcomes
- Fewer resources
- Greater mental health needs in our young people
- Fewer services to support children and families
I believe that we need a different type of school leadership, a different kind of teacher.
Teachers and leaders are still trapped by the exam treadmill, still unable to have in-depth curriculum discussions or spend proper time collaborating.
Imagine if we flipped the story and leaders and teachers were designing the curriculum, to better match modern societal needs with an intelligent approach to assessment alongside it.
I suggest that neurodivergent thinking is a great way to flip any story.
3. Creative thinking
Take impulsivity, one of the main symptoms of ADHD. The studies suggest it might lead people to have more original ideas. That’s because people with ADHD often lack inner inhibition. This means they have trouble holding back when they want to say or do something.
Many of my neurodivergent clients have found a new voice and new priorities, including giving attention to staff wellbeing and rethinking the micro-management that characterises so many schools. But achieving this small-scale will not have the impact we need it to have and they often do this at the cost of risking their career.
Women with ADHD, in my experience, tend not to fear the truth and make brilliant cases for what new approaches might look like when systems are broken. More importantly, they often have the drive to see it through. This can appear radical, stubborn even, but for us it’s just about doing what makes sense.
In my book, the Unhappy Headteacher, I explore ways we can still have influence and find joy in the role – because I believe we can. I also believe the system needs drastic change with an uncompromising model of implementation. To me, it is clear that neurodivergent women have a valuable part to play in this.
And gender does matter here. According to Association for Adult ADHD (AAD) men with ADHD are likely to develop aggressive and defensive behaviours in response to being misunderstood, Whereas women with ADHD are more likely to mask and experience self-doubt. This self-doubt can be a gift in headship as with support, it is the place where growth and empowerment can be found.
What all adults with ADHD do have in common, in my experience is inner steel. We find EVERYTHING hard and to find fulfillment and do the stuff that lights us up – like pursuing excellence for a school – we have to accept that we will face tremendous amounts of challenge. Mostly because others often misunderstand our intentions. We share a bounce-backability that is unique to neurodivergent leaders and has prepared us well for the current state of affairs. When everything is hard anyway, dealing with the funding crisis seems surmountable somehow – leaders with ADHD believe there is a way to do the impossible, we just need to find it and we know we can
4. Representation
And let’s not forget the importance of representation in all of this. I have a client who has a diagnosis for autism and fears being open about this with her seniors because of her perceived risk of not being considered for promotion. This saddens me when I think about how far we still have to go in exposing our students to the talent and capability of people with ADHD. Our young people deserve to see examples of adults like them leading schools successfully yet as a culture we still shy away from celebrating the gifts of ADHD – these ‘gifts’ scare us rather than inspire us – what message does that give our young people with ADHD and what potential are we stunting?
Neurodivergent students need opportunities to learn ways to manage the challenges associated with serial rushing and extreme procrastination – what better way to do this than having high-performing leaders with ADHD modelling this around them.
My son has an EHCP and was recently interviewed by an Ofsted inspector in his college who asked him why he thought he’d been so successful at 6th Form, after performing below average at all other stop-off points. Lucas cited the single most important factor as being taught by a maths teacher who is autistic and comfortable with it. Could it be true that to become a mathematician, Lucas needed to see someone like him in the role first? And if so, what does this say about representation among our teachers and leaders in schools?
So how can we utilise neurodiversity in shaping the future of schools?
- Create a climate where neurodivergent school leaders feel free to be unapologetically themselves
- Celebrate neurodiversity in schools and society
- Recognise behaviours associated with ADHD and get excited about them as a sign that creative thinking is taking place
- Follow women with ADHD – they have survival mechanism we need right now in schools
'Coaches Like Us': You Have to See It To Be It

Written by Hannah Wilson
Founder of Diverse Educators
‘You have to see it to be it,’ the quote from Billy Jean King, is a phrase we hear used a lot to challenge the lack of visible role models in society but also in our profession.
It is widely agreed that diverse representation is needed in every layer of the school system.
Our trust boards and governing bodies, our CEOs and Headteachers, our Senior Leader Teams are all people spaces that need diversifying. Alongside reviewing representation in our curriculum and in our libraries, for our learners, we also need to review it for our staff. (This is why we host a #DiverseEd World Book Day event each year to amplify authors from our network).
There is a lot of continuing work to be done to disrupt, to dismantle, to diversify these different spaces and to review who gets to occupy them.
But there are other educational spaces for us to also review:
- Who recruits, develops and mentors our trainee teachers?
- Who recruits, develops and mentors our early career teachers?
- Who recruits, develops and mentors our aspiring leaders?
- Who recruits, develops and coaches our existing leaders?
When you review these spaces you will often find a homogenous team, a team who mainly hold majority identities.
So how are the trainers, the mentors and the coaches being trained to become conscious of their own identity, to become confident in addressing their own privilege and to become confident in disrupting bias in the many forms through which it can manifest?
How trauma-informed are the trainers, the mentors and the coaches in supporting individuals who have experienced identity-based harm?
The Church of England Foundation for Educational Leadership launched a brilliant pipeline programme to nurture leaders from a global majority background called Leaders Like Us a couple of years ago, in partnership with Aspiring Heads and the Institute for Educational & Social Equity. This programme is a gamechanger for our education system and our future workforce.
So let’s all consider what Trainers… Mentors… Coaches … ‘Like Us’ would look like.
If we put a spotlight on ‘Coaches Like Us’ as a school, college, trust, SCITT, Teaching School Hub and localities we need to ask ourselves:
- Who gets to be coached?
- Who gets to be The Coach?
- Who gets invested in?
- Who gets nurtured to flourish?
- Who gets supported to progress?
And most importantly, do people get to choose their coach? Or what has become a common phenomenon – does a coach get chosen for them?
Coaching is about creating a safe space. About having a confidential conversation. About exploring how one is feeling. About being vulnerable and open. If your coach is your line manager or someone you work closely with – someone who might appraise your performance or sit on a promotion panel – we are in muddy waters.
What difference would it make for an aspiring leader to self-select a coach who resonates with them? A coach who shares their identity? A coach who has walked their walk?
Some final thoughts:
- How might being coached or becoming a coach help diverse educators stay in the system?
- How might being coached or becoming a coach help diverse leaders climb up the leadership ladder?
- How might being coached or becoming a coach help us tackle the glass ceiling and the concrete ceiling in the education system?
To help our clients, who have asked for our support in diversifying their coaching pools, we have created a #DiverseEd Coaching Directory:
- You can find 25+ coaching profiles here.
- You can meet our coaches through our video gallery here.
- Get in touch if you are a coach who would like to be added or if you are looking for a coach and would like to be connected here.
Is there a hierarchy of protected characteristics?

Written by Hannah Wilson
Founder of Diverse Educators
One of the questions we regularly ask in our DEI training for schools, colleges and trusts is which of the protected characteristics are visible within your context.
This question is deliberately wide and can be interpreted in a couple of different ways:
- Which of the 9 PCs are visible? i.e. which ones can we see as some are hidden/ invisible.
- Which of the 9 PCs are visible? i.e. which are present in our community and thereby which are missing or do we not have/ know the data to confirm they are present.
- Which of the 9 PCs are visible? i.e. which are being spoken about, invested in, have we received training on.
Often people ask do we not mean – which is a priority? And we emphasise to focus on visibility and explain the gap between intention and impact as there is likely to be some dissonance between what is happening and how it lands.
The reflections and discussions across a full staff will surface some of the disparities of what is being paid attention to. Moreover, it will also highlight the difference in perspectives across different groups of staff – groups by role/ function and groups by identity.
A key thing for us to reflect on, to discuss and to challenge ourselves to consider is that there are nine protected characteristics – so are we thinking about, talking about, paying attention to all of them simultaneously? Are we balancing our approach to create equity across the different identities? Are we taking an intersectional lens to consider who might be experiencing multiple layers of marginalisation and inequity?
We encourage schools to lean into DEI work in a holistic and in an intersectional way, as opposed to taking a single-issue approach as our identities are not that clean cut. We worry that some organisations are focusing on one protected characteristic per year, which means that some people will wait for 8-9 years for their identity to be considered and for their needs to be met. This is also a problem as we generally spend 7 years in a primary context and 7 years in a secondary context so all 9 would not be covered in everyone’s educational journey.
Trust boards, Governing bodies, Senior leader teams do not sit around the table and decide that some of the protected characteristics are more important than others, but there will be a perception from outside of these strategic meeting spaces that there is a hierarchy. i.e. different stakeholders will have differing opinions that in this school we think about/ speak about/ pay attention to/ deal with XYZ but we do not think about/ speak about/ pay attention to/ deal with ABC.
Another thing to consider about the perceived hierarchy is regarding which of the protected characteristics we are expected to log. If all 9 of the protected characteristics are equal, why do schools only need to log and report on two of them for the pupils’ behaviour and safety – we are expected to track prejudiced-based behavioural incidents of racism and homophobia? Does this mean that transphobia, islamophobia, ableism and misogyny are less important? Does this mean we are holding the student to account but not the staff?
One solution to this specific imbalance is to move from a racist log and a homophobia log to a prejudice log. A log that captures all prejudice, discrimination and hate. A log that captures all of the isms. A school can then filter the homophobia and racism to report upwards and outwards of the organisation as required, but the organisation’s data will be richer and fuller to inform patterns of behaviour and intervention needs.
CPOMs and other safeguarding and behaviour software systems enable you to tailor your fields so see what capacity yours has to add in extra fields. You can then log all prejudice and track for trends but also target the interventions. We have been working with a number of pastoral leaders and teams this year to grow their consciousness, confidence and competence in challenging language and behaviour which is not inclusive and not safe. We are supporting them in making their processes and policies more robust and more consistent to reduce prejudice-based/ identity-based harm in their schools.
Another consideration alongside the student behaviour logging and tracking is to also consider the logging of adult incidents. Do our people systems capture the behaviours e.g. microaggressions and gaslighting that the staff are enacting so that these patterns can also be explored? Do our training offers for all staff, but especially leaders and line managers empower and equip them to address these behaviours?
So as we reflect on the question: Is there a hierarchy of protected characteristics?
Consider how different people in your organisation might answer it based on their unique perspective and their own lived experience. And then go and ask them, to see how they actually respond so that you become more aware of the perception gap – if we do not know it exists, we cannot do anything about it – and the learning is in the listening after all.
Safeguarding Inclusion: Nurturing Diversity in Educational Settings

Written by Caroline Anukem
Caroline Anukem is Equity, Diversity and Inclusion Lead at Beaconsfield High School in the UK. She is a driving force, a change-maker, and a relentless advocate for equity.
In the intricate cosmopolitan British society, the journey of being black and British often interconnects with the educational landscape in profound ways. From the halls of primary schools to the lecture theatres of universities, the quest for inclusion and diversity shapes the experiences of students and educators alike. As someone who has navigated this first-hand, I have come to understand the vital role that practice and policy play in safeguarding the well-being and success of every individual within these institutions.
Reflecting on my own educational journey, I recall moments of both triumph and tribulation. From the early days of primary school to the complexities of university life, I encountered an array of challenges and opportunities that shaped my sense of self and belonging. In the midst of this journey, the importance of representation and inclusivity became abundantly clear. Seeing individuals who looked like me in positions of authority and influence instilled a sense of pride and possibility, while the absence of diverse perspectives served as a reminder of the work that still needed to be done.
When I applied for the role of Equality, Diversity, and Inclusion (EDI) Lead. Initially, it struck me as a novel and innovative approach to promoting inclusivity within the educational setting. However, as I delved deeper into the role and its implications, I came to realise the profound parallels between EDI and safeguarding.
Just as safeguarding measures are in place to protect the physical and emotional well-being of students, EDI initiatives serve to safeguard the diversity and inclusion of all individuals within the educational community. From ensuring that curriculum materials reflect a diverse range of perspectives to implementing policies that promote equality of opportunity, the role of an EDI Lead is multifaceted and far-reaching.
In many ways, the principles of safeguarding and EDI are intertwined. Both prioritise the creation of safe and supportive environments where individuals feel valued, respected, and empowered to thrive. Just as safeguarding protocols employ a triage system to prioritise the most urgent needs of students, EDI initiatives must also adopt a strategic and targeted approach to address the unique challenges and barriers faced by marginalised communities.
One of the most profound benefits of a truly inclusive and diverse educational environment is the transformative impact it has on individuals and communities. When students see themselves reflected in the curriculum, when they encounter diverse perspectives and experiences in the classroom, it enhances a sense of belonging, wellbeing and empowerment which will ultimately correlate to improved academic achievement. It cultivates empathy, resilience, and a deep appreciation for the richness of human diversity.
As an EDI Lead, my role is not just about implementing policies and practices; it is about embedding a culture of inclusivity and respect that permeates every aspect of school life. It is about amplifying the voices of marginalised communities, challenging systemic barriers, and championing the rights of every individual to learn and thrive in a safe and supportive environment.
The journey towards creating truly inclusive and diverse educational settings is a collective endeavour that requires commitment, collaboration, and courage. This has prompted Beaconsfield High School (BHS) to take the bold step of hosting our first EDI conference in April this year. We will focus on highlighting the parallels between safeguarding and EDI. We will strive to communicate better understanding of the interconnectedness of these principles and the profound impact they have on the well-being and success of students.
In conclusion, the journey from the simplicity of my village education in Liverpool to the vibrant inclusivity of BHS is a testament to our progress. Yet, it serves as a reminder of how much further we can go. As an EDI Lead, my commitment is to develop a learning environment thriving on differences, not just educating minds but nurturing hearts, building lasting friendships, relationships and encompassing the British Values in our daily practices. The journey toward a more inclusive and equitable educational landscape continues, one story at a time.


