Student leadership programmes and celebrating diversity: students as drivers of change

Written by Sadie Hollins
Students are drivers of change. As educators I’m sure we can all think of times when students have been the key stakeholder that affected positive change in our schools, whether that be at the classroom level or at a schoolwide level. I have felt fortunate to witness a number of our students make a stand, whether it be fighting for the rights of the student body as a whole, or coming together to support a member of their peer group facing a particular challenge, such as ‘coming out’. This is student leadership.
I have been in awe of what our Student Council has been able to achieve in terms of the quality of events they plan and host, and the fundraising projects they have created. As well as how the Student Executive Board works together along with class and year group representatives for the Student Council to discuss ideas and how they might be implemented in the school. This is student leadership.
Students drive change.
It struck me recently that often this instinct to drive change comes intuitively to students. School is such an important and informing experience for young people to learn about leadership, and for some may be the only ‘organisation’ they experience being a part of until they reach university or work. How we define leadership, and how we lead as staff, will indirectly inform students how leadership works. For better or worse.
Schools offer many leadership opportunities for students to be a part of, including captaining sports teams, editing school magazines, holding positions such as prefects, student mentors, peer tutors, Student Council members, and many more. However, a lot of these opportunities tend to be most readily undertaken by students that excel in some form, whether that be academically, socially, or physically. A lot of the time students that take on these roles are the ‘good’ students. This in turn can send a message to other students about what leadership is. Leadership is for ‘good’ students.
A lot of these roles don’t come with any ‘Leadership’ training for the role, so it’s often implied that you learn by doing. Whilst I think there is a lot of merit to this approach, I feel that if we work with students to help them define what Leadership means to them and help them (all of them) develop their skills, perhaps we can empower a bigger portion of our student body to drive change.
Last year we started 2 different Student Leadership programmes (Level 2 and 3 Leadership programmes from Sports Leaders UK) in our school. We’ve just begun the Level 2 course with our new Year 11 cohort, and this week we got students to rate themselves according to the different Leadership skills outlined in their course booklets (communication, teamwork, organisation, problem-solving, etc). One of the areas that they had to rate themselves on, and explain a little more why they had given themselves their score, was ‘self-belief’. When going around and looking at their work I was struck by how many students had rated themselves so lowly in this area (scoring themselves less than 5 out of 10) which made me feel a little sad. How can students drive change or lead (or push themselves forward in whatever they choose) if they don’t believe in themselves? We can’t ‘magic’ ourselves into developing a greater sense of self-belief, but we can gain it through experiencing challenges and getting through them (imperfectly). I also wonder if this lack of self-belief sometimes comes from comparing ourselves to the narrow view of what a successful student (or adult) is – normally the best of the best.
The hope for our leadership course is that we can challenge students to redefine what a good leader is, and for them to realise their own leadership potential. We all need and want different types of leaders for all types of situations – we just need to empower students to believe that they could be the leader that someone else needs.
In order to create a school (and organisation) that appreciates and celebrates diversity, we need to empower students to feel confident in who they are and drive the change they wish to see. Our job as teachers is also to be genuine and open about who we are, and model to our students that we all have the ability and power to affect positive change.
‘Is she Somali?’

Written by Baar Hersi
‘Is she Somali?’
This is the question I repeatedly hear in my first term in a new school. I hear it in the corridors, I hear it in their whispers and I hear it when I enter a classroom. This has been my normal for the past decade.
It is so humbling to witness that moment of anticipation, where I get a glimpse of what my answer might mean to them. The question above may seem like a simple question, one born out of curiosity or just kids being nosy, but it is actually far more profound than that. The real question these students were asking was ‘Is she me?…..because if she is me then I can be her.’ Each time this question is asked it is loaded with hope because we know, they can’t be what they can’t see. The reactions on my students’ faces when I answer ‘YES’ is one of the reasons why I became a teacher.
This question empowers me. It gives me superpowers to show up and overcome the challenges I face because there is no greater fuel and purpose than empowering a young person and giving them the permission to be themselves. No one gave me that permission during my school years, 11 years old Baar felt like that alien that no one can relate to but tolerated. I was a freshy for some, not black enough or holy enough for others and too foreign for most. I spoke three languages, performed in front of packed out theatres and could banter for days. I am a people’s person but I didn’t belong in that space. Bless my teacher, Ms Gleeson, who created a safe space for a young immigrant girl overwhelmed by her new adopted country. It took me years to be empowered, to be me and to feel like I belonged at school. I owe this to my mum, who fought for me and siblings to be safe and brave in our new home.
‘Is she Somali?’
This question is my why!
It is why I use my voice and experience to advocate for parents who struggle to navigate the education system and work tirelessly to bridge the gap between school and home. It is why I organise cultural events to instill pride in young people who for far too long have heard only negative narratives about their identity. It is why I donate books written by Somali authors to our school library and use my network to invite Somali professionals to be our guest speakers and mentor our students. I want to empower the next generation to ensure that their experience is different from my generation’s or even my own children who have never been taught by a black teacher (let alone a teacher of Somali heritage) in secondary school in one of the most diverse boroughs in London.
We often talk about the importance of inclusion and representation and how important it is to have a staff body that is reflective of the students in a school. For me representation is more than whether or not the staff reflect the student they teach. It is about ensuring that students do not feel invisible in their own school. I have found that it is very possible to belong to one of the largest ethnic groups in a school but not see one poster of someone who looks like you. Schools are meant to be where possibilities are planted. Schools are meant to be a conduit for aspirations and inspirations but this is not the case for many BAME students. We really have a very long way to go.
Many of my students are shocked when I tell them about my friends and networks which consist of Somali writers, doctors, lawyers, creatives, councillors, engineers, lecturers, teachers, film makers, health professionals, athletes and so many other distinguished professionals and leaders. I cannot count the number of times a young adult has told me that they wish they had a teacher like me. I think they mean someone who they can see themselves in. I would like to think they mean someone who is confident with her identity, who is driven by her values, who feels empowered to be authentic and is willing to open the BHM fashion show in her traditional attire in the first half term in a new school. Yes…..I did that!
So if my representation, my narrative and my journey to self-empowerment helps empower another young person then I look forward to answering….. ‘Is she Somali?’
The complexity of diversity: negotiating “possible spaces”.

Written by Kathryn Kashyap
Teachers often ask how they can approach the learning of pupils who are designated with more than one “label”- for example EAL, SEND and “disadvantaged”. Looking at how to recognise and create “possibility” with all pupils in the spaces where they learn takes the focus away from within-child deficit views. Instead, it makes us look at our practice and listen to our pupils about what works for them. Here I set out how this idea of “possible spaces” can help us address the complexity of diversity.
Firstly, it’s important to interrogate the labels that are being used, challenging negative assumptions around race, gender, class and disability. On further investigation, we find that pupils’ learner identities are far more complex than “just” EAL, SEND and disadvantaged. It’s important to understand which black, Asian or other minoritised ethnic background they are from, and which (if any) religion they follow. Some families may be dealing with the trauma of fleeing from war or persecution. Their family may be living in a working-class context, but from a different socio-economic status in their home country. Post-migration, they may be facing significant challenges. There are also in-depth questions to consider about the aspects of SEND that teachers have identified or are suggesting might be present. Alongside this we need to understand how academic English language acquisition, multilingual learning and for some the impact of disrupted formal education, both in the UK and prior to arrival, can be supported.
Then, we need to talk with the children and young people we are teaching. For my research, I asked a group of Somali young people who had migrated to the UK, and who were considered to need extra support (whether due to EAL, SEND, disadvantage or “underachieving”), where they felt they learnt best, with whom and why. What came across very powerfully was their frustration and for some their anger about how they were often treated as “behind” or even as “unable”. Their knowledge and experiences were ignored within a monolingual, mono-cultural curriculum. Their needs were side-lined or only met partially. Their hopes for making progress were squashed by systems that held them back.
These young people pushed back forcefully. They sought out spaces, both formal and informal, where they could learn, with teachers, mentors or peers who recognised their skills and knowledge, who believed in their potential, cared about their wellbeing and could advocate for them. Often this was about building confidence. Teachers asked the pupils what they knew rather than assuming they didn’t. They used talk, not reading as a way into learning. They drew on their strengths whilst supporting specific aspects. They challenged them and expected them to aim high.
Where these possible spaces existed was not clear cut, however. A lesson could be successful one week and not the next, or a session could shift moment by moment. This could be due to the teaching strategies being used. It could be that the topic was seen as especially difficult or irrelevant, or the pressure to get through the curriculum felt overwhelming. The pupil might be sitting next to a supportive peer one lesson and moved the next.
Acceptance was also a vital aspect of possible spaces. Managing to study and gain the help they wanted without being seen as a “neek”, whilst resisting being seen as unable, was complex. Bending the class rules, but just enough to get a small warning from their supportive teacher. Being the class joker to cover over difficulties with written literacy (but at the same time giving their peers great ideas for their story). “Forgetting” homework when they couldn’t access it. Copying surreptitiously from a neighbour. Arriving late for a lesson which they felt even before they began was going to be a failure due to lack of appropriate support. All tactics which could be interpreted as the pupil being disruptive or disinterested in learning, when in fact they were anything but. Asking “why” in these situations was key to unlocking possibility.
The idea of possible spaces is that it cuts across the anxiety that many of us have as teachers that there are strategies “out there” where pupils are labelled in more than one “category” that no one has told us about that, if we knew them, would solve the problem. It focuses on deepening our relationship with the pupil, looking at what works for them and replicating this across the curriculum. It draws on their knowledge, skills and interests and puts them at the centre not the margins of our planning. It reminds us that when they or we have an unsuccessful lesson, we can look outward at what was happening in the learning space, not inward at deficit or failure. And usefully, given the turn to tuition in the government’s “catch up” strategy, it emphasizes the importance of all mainstream lessons being “possible” spaces.
My Five Top Tips for Making Your School LGBT-friendly

Written by Jared Cawley
LGBT (lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender) Pride month seems like a very appropriate time to give extra attention to making sure your school is an inclusive, diverse and safe place for your families, students and workforce who identify as LGBT+. The month of June honours the anniversary of the 1969 Stonewall riots, where LGBT people and allies fought against police brutality and harassment that many were and continue to be subjected to today.
Schools are well-known for their openness and celebration of diversity when it comes to students, but some LGBT teachers still feel isolated and uncomfortable to talk openly about their sexuality. Schools are heteronormative workplaces and being a person who is not ‘straight’ requires some careful navigation. Headteachers and school leaders have a responsibility to sustain a school environment that welcomes diversity, supports equality, and defend all staff, including those who identify as LGBT. If you are a school leader who identifies as heterosexual, or is not part of a minority group, you are less likely to notice the exclusion or the discrimination that may be happening in your school.
As a LGBT teacher and a gay man, I have been subjected to abuse and discrimination throughout my life for loving someone of the same sex. Even though Government legislation has strengthened over the last few years, there is still a long way to go. As a LGBT teacher, I am hypervigilant and cautious about who I ‘come out’ to. This feeling of uncertainty is because being straight is the preferred and presumed sexuality. Choosing to ‘come out’ to students, families and colleagues is fearful, as you do not know their opinions and beliefs when it comes to the LGBT community. Making your school LGBT+ friendly must begin with small, deliberate steps. We must acknowledge that this will not happen overnight, but with thoughtful planning and strong leadership, a school can improve its culture of inclusivity for everyone.
When making cultural change in your school, it is important to avoid tokenism. It is superficial to teach diversity for a week or a month as a bolt on to your curriculum, when that is the only time you discuss LGBT rights or teach how to be anti-racist. All members of your school community is needed to make real change, deliberately walking the walk, instead of just talking the talk.
Below are my five top tips for making your school LGBT+ friendly:
1 Use Inclusive Language
Making small changes around inclusive language can have a huge impact on either making people feel accepted and/or feeling excluded.
Here are my suggestions:
- Instead of greeting your staff team or students with, ‘Good morning ladies and gentlemen, boys and girls’, say, ‘Good morning everyone’. With this, you have included all genders and identities without assuming everyone identifies with the gender they were assigned at birth.
- Challenge students and colleagues who continue to use phrases that diminish showing emotion or acting like a particular gender. For example: ‘man-up’, ‘you throw like a girl’, and ‘boys don’t cry’.
- Stop organising students into boys’ teams and girls’ teams, find different ways.
- Avoid reinforcing gender stereotypes.
2 A LGBT+ friendly school is everyone’s responsibility.
- It is a mistake to think that creating a LGBT+ friendly school should solely be the responsibility of the ‘gay teacher’. It should be a collective responsibility. Headteachers, senior leadership teams, teachers and the rest of the school community should be actively working together to promote an inclusive and diverse environment, ensuring all members of staff and students feel safe and can be their authentic selves.
- CPD and INSET days could involve external speakers, offering your staff a refreshing voice and a different perspective.
- LGBT+ people experience the world differently to their heterosexual counterparts, and school leaders should give them a safe space to talk about their experiences, with the support of their LGBT allies.
3 Be Proud of LGBT Visibility
If you are showing a prospective same sex family around your school, or a LGBT teacher comes for an interview, or a new student who may identify as LGBT or does not know their sexuality, how do they know that this school or future workplace is a safe and inclusive environment where they can be their authentic self?
Here are some suggestions:
- Give teachers a choice to wear LGBT badges/pins or have LGBT lanyards
- Display the Pride flag inside and outside your school. There are many flags here that represent the LGBT+ community.
- Displays. Show your visitors that you celebrate inclusion and diversity. Have displays celebrating LGBT stories and issues.
- Encourage LGBT+ teachers to make a network or support group where they can talk about LGBT issues and use this to show that LGBT+ voices matter.
- Have your senior leadership team and staff go on a learning walk, where the focus is LGBT inclusion. Can you see it represented in your school?
4 Have an inclusive and diverse curriculum
Your curriculum should be well planned and deliberately tailored to minority groups and should not be left to chance. To avoid tokenism, these practices should be carefully planned and seen across all subject areas.
Here are some suggestions:
- Children’s story books should include and promote different family dynamics, including same sex couples, single parents, foster parents, disabled children and parents, families of colour, families of different religions. Here are some ideas.
- In mathematics, have word problems that are inclusive of same sex families. Instead of Mrs. Smith or John, have names that come from a range of countries and heritages.
- In your presentations, ensure that the pictures you use show a range of minority groups.
- In your humanities curriculum, teach about colonisation, the impact of imperialism, and celebrate indigenous communities and customs. See here for more about decolonising your school curriculum.
- Diversify your set texts, offer a range of authors, not just white, heterosexual men.
5 Educate Yourself
I believe the best way to learn more about the LGBT community is to educate yourself, have an open mind and be comfortable with being challenged. I feel there can sometimes be a fear about people who do not belong to a certain minority group, making a mistake or unconsciously offending someone, or using a term or acronym that is outdated.
Here are my suggestions:
Read books and use organisations that specifically discuss LGBT voices in education and whole school approaches:
- Catherine Lee’s ‘Courage in The Classroom. LGBT Teachers share their stories’.
- Shaun Dellenty’s ‘Celebrating Difference. A Whole School Approach to LGBT+ inclusion’.
- Andrew Moffat’s book series for the No Outsiders programme.
- These organisations offer a plethora of teaching resources: Schools Out, Stonewall Education, Mermaids UK, LGBT Ed, and The LGBT Primary Hub.
- The LGBT Primary Hub offers a snappy timeline of our history and glossary of LGBT vocabulary.
Did you think being a female leader was tough? Try being a diverse one.

Written by Susie Fernandez-Gomez
Med in Educational Leadership, Head of MFL and SLE
There are studies concluding that race and gender may interact to shape different dimensions of women’s employment experiences. Therefore, understanding the interlocking system of intersections is key to addressing diversity challenges in education. The theory of intersectionality articulates a framework which can help address the challenges that minority women face with regard to their identities and their experiences. When race and gender act as a barrier, minority women in leadership positions may face specific challenges which are often unmet by others.
I am one of those women. What some would class as the ‘too different type’ of leader.
According to research, women have developed values and beliefs that translate into specific behaviours. Women are considered to socialise to show feelings, compassion, patience and intuition. This has led to a judgement that all women need to showcase these attributes in order to become effective leaders. One could argue that this list of values and skills would be ideal if it wasn’t for the fact they have actually become barriers which women have to overcome to become leaders.
I am one of those women. What some would class as the ‘soft type’ of leader.
On the other hand when women display attributes such as strength in character, being passionate about their own views, the ability to ask difficult questions or relentlessly having high aspirations from their followers as well as their own leaders, frustratingly, there is still a tendency to class these women as difficult and scary.
I am one of those women. What some would class as the ‘hard type’ of leader.
At this point you are probably wondering:
How can she claim to have all these attributes at once?
I will answer your question by posing another:
How could anyone become a leader and not be a mixture of all those attributes?
Surely if you offer different views, can support and empathise with your followers at the same time as showing the strength needed to lead them and challenge the establishment, would that not make you a true leader that can connect pretty much with any type of follower?
It would seem not…
I have faced great challenges when attempting to reach senior leadership positions. In particular, I believe that cultural variations exist in terms of expectations of leaders. Kuckhohn (1951) defines culture as a pattern or way of thinking, feeling and reacting in specific situations. Culture signifies values, ideas and symbols. Leadership expression may therefore vary based on the values, practices and symbols followed by individuals within a society. Societies may support either masculine or feminine values. Societies like the UK which support feminine values are found to balance masculine traits like aggression along with feminine traits like cooperation and collaboration. When leaders from different cultures co-exist, it can lead to potential challenges regarding how a leader should behave.
I am one of those leaders who happens to be culturally different. That combined with being a woman that shows ‘soft’ attributes as well as ‘hard’ characteristics, which only male leaders are praised for, makes me a bit too weird, I suppose…
The truth is that many women, just like me, who attempt to reach senior leadership positions will need to balance potential biases from various levels. One such bias is expectations of specific qualifications and extensive experience, especially among those of different racial origin. The average white British male aspiring leader already has the most valued qualification desired for senior leadership that there is: the nationality and the gender. In regards to experience, as long as he can show potential, the box would have been ticked. Why not apply for the job, hey?
I am one of those leaders who is not British nor male so my lists of qualifications and proven experience do have to be quite extensive, indeed. Why would I dare applying for the job, really?
I have often felt that my non-Britishness has been a factor which has led to such lack of opportunities.
Diversity is key to education leadership, as the intersection of different characteristics may highlight some systemic challenges faced by leaders. Awareness and alertness exhibited during communications, along with insight into the rules, practices and conventions to be followed in various settings, are often more evident when there is diversity in leadership.
Moreover, diverse leaders may respect the cultural differences of their teachers and remain well-informed about the various cultures. Therefore, a diverse leader may define the roles and responsibilities of the members while acknowledging differences in expectations. Communication management and trust are important factors which support success in institutions that have diversity in their leadership positions.
Time has come for schools to understand the benefits of diversity leadership. Diversity in leadership is key as it can enhance a wide range of views and opinions. It has also been argued that such different perspectives can help in problem solving. By supporting diversity in leadership, it is possible to improve self-efficacy, resilience and self-management. Research has also identified that by enhancing trust-based accountability rather than test-based accountability, it is possible to enhance the quality of outcomes.
Women leaders are considered to establish better morale and therefore are able to achieve better results. A preference for diverse women leaders can help achieve such trust-based accountability. Diverse women leaders are considered to provide better support for employees. This can in turn mean that teachers are provided with independence, agency, and an ethical and righteous purpose, along with a trust-based accountability system.
I am one of those leaders whose team respect and love in equal measures, I can proudly say.
The key component to development of leadership is by establishing an identity as a leader. However, for the female leaders, it has been argued that the failure to include the discussion of the identity and the gender identity especially related to the leadership identity development can lead to additional challenges. The failure to discuss the issues with gender identity and its effect on the identity and the leadership can be essential to understanding credibility in a culture that is deeply impacted by the external environment.
Through the entire process of leadership identity development, the female leaders may be asked to prove their credibility as a leader. As a diverse female leader, at various junctures of my career I have been asked to mellow down my ‘Mediterranean’ ways.
I am one of those leaders who has said NO. This is who I am and I will stand united with many other diverse female leaders out there who, I am sure, have some stories to tell about their own tough journey.
The Absence of Diversity in the Literature Curriculum – and its Lasting Impact

Written by Anjum Peerbacos
20 years experience as a teacher
Riz Ahmed made a powerful speech regarding diversity in the Arts: http://www.independent.co.uk/arts-entertainment/tv/news/riz-ahmed-warns-parliament-that-lack-of-diversity-in-tv-leads-people-to-isis-a7610861.html Riz Ahmed warns Parliament that a lack of diversity in TV is leading people to Isis www.independent.co.uk
He stated that if young people could not see themselves as part of the narrative or the mainstream representation, they would turn elsewhere to feel that they had a sense of belonging. He said it was the responsibility of the Arts to reflect society; to reflect the patchwork that makes up a wider world, and our global community.
In so many ways, Literature is another Art form and should be doing the same. When we study texts in class, there should be an opportunity for students to be able to see themselves in the literature world. However currently that is not the case.
For more than two academic years now, I have taught the new GCSE curriculum for English Literature, I have taught ‘Lord of the Flies’ by William Golding, ‘An Inspector Calls’ by J.B Priestly, ‘A Christmas Carol’ By Charles Dickens, ‘The Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde’ by R.L Stevenson, and ‘Romeo and Juliet’, by William Shakespeare. White males that are no longer with us, have written all of these texts.
It may be that because I work in a boys school that these texts have been chosen, as the demographic of the school is largely white and male; however one could argue that in such circumstances it is vital that we expose our young people to the width, and breadth of the spectrum of the society in which we live. Students regardless of demographic and gender should be exposed to a range of writers’ experiences and Literature. It broadens their horizons, and ultimately their experiences. Students have studied the above texts, in addition to a small collection of poems largely about war, with the anecdotal inclusion of Benjamin Zephaniah and John Agard. ‘The Conflict Cluster’ largely addresses the atrocities of war, and as a result these young people have not been exposed to the wealth of Literature that exists in the world.
Across the exam boards, the choices have been extremely narrow. There are few women and even fewer texts from a diverse or BAME background. I appreciate the need to study the works of Shakespeare but, not counting The Bard, on the AQA specification there are 19 opportunities to explore other Literature texts and only 2 are from non-White authors.
On the Edexcel specification there are 15 opportunities to study a text written by a white male, there is only 1 non-White BAME author. On the Edexcel specification, all White Male playwrights write the Modern Drama Texts. WJEC offers two options which are non-White authors, however is more inclusive of female writers over time.
Obviously, I understand that we want children to study, learn and love Shakespeare and he is a white male and is from the 17th century. There is one re-occurring BAME author for modern prose and that is Meera Syal and her novel ‘Anita and Me’, and I can’t help wondering how much of a token of her appearance on the curriculum is.
My other concern regarding the curriculum is does it need to be British? And is there a place for Modern World Literature or modern world prose or drama? Why are we limiting our young people to English British largely male Literature, which is no longer representative of the global world in which we all live?
In addition, what constitutes British Literature? Is Syal considered English Literature or British Literature? Moreover, why are we not considering the likes of Malorie Blackman? Blackman is a modern Black female author and is much needed. She addresses many sensitive issues within her texts which provide the debate needed, which would also meet the Social Moral Spiritual and Cultural (SMSC) criteria, which Ofsted demands of schools.
I happen to work in a boys school, and I am teaching an entirely male curriculum, bar a few poems in the poetry anthology, and my worry is that these boys are going to live, work, learn and prosper and flourish in a world which includes men and women. A world, which includes the young and the old. A diverse world which includes people from all walks of life. So why is our Literature curriculum not reflecting this and preparing them for the alternative view? For the different perspective? For the obscure or the distance or the far-reaching? Why is it so inward looking and insular? Surely, this is then a potential breeding ground to consider anything different as ‘The Other’? How is this progressive?
As Ahmed stated the Arts should be a representation of the world and narrative in which one can see oneself. Why aren’t ‘we telling these kids they can be heroes in our stories, that they are valued’? Ahmed goes on even further to state that if a young person cannot see themselves in the wider narrative then ‘we are in danger of losing people to extremism’. I think he makes some valid points. If you are studying a text for six weeks in a classroom, and potentially over five years you do not find yourself represented in any of those stories, then is Ahmed making a wider point? Do we not have a responsibility to deliver a narrative which is outward looking and less insular?
The curriculum was developed under Michael Gove, https://qualifications.pearson.com/en/qualifications/edexcel-gcses/english-language-2015.html
and I feel as though he has been able to dictate a curriculum, which he saw fit in an era, which is no longer fitting or applicable to our young people now.
The issue has been raised before, however I feel that now more when students are asked to regurgitate texts in exams, texts that they may not be able to relate to, or even understand, it has become a more pertinent issue. In light of recent events where we have witnessed a rise in hate- crime, communities feeling isolated and marginalised, immigrants being targeted; I think that now more than ever our young people should understand a wider broader spectrum of literature appreciating and celebrating difference and diversity. Of course, there is a place for Shakespeare and Romantic poetry, and of course, there should be an appreciation of the likes of Dickens and Austen. However, should there not be an opportunity to experience World Literature?
Our young people are interacting on a global platform and developing a global community. If I were a young person living in 21st century Britain, I would not think the Literature that I am exposed to on the current curriculum is in any way reflective of me, or the world in which we all live.
Why Diverse Representation Matters in Children’s Books

Written by Orla McKeating
Entrepreneur, coach and motivational speaker
I started Still I Rise Diversity Story Telling for Kids in 2019 as a passion project as I really didn’t see enough representation in kids’ books. As a single mother of a bi-racial child I had learnt the importance of this for the well-being, influence and mental health of this for children, but I didn’t imagine the impact this would have on so many young people around the world. Still I Rise is now a global business, lockdown forced us to do virtual storytelling sessions which has massively built our community and the feedback we have received from parents, psychologists, teachers and the kids themselves has been incredible. And having worked with hundreds of children globally we can see the impact first-hand of the importance of diverse and inclusive books, how it builds confidence, empathy skills, how it inspires and creates impact and allows for deeper connections with society as a whole.
I was blissfully unaware of the importance of a diverse and inclusive world having been brought up in largely white Northern Ireland into a family of privilege and shielded from the Troubles we experienced until I was in my late teens. I lived in Belgium for 10 years post university in a culturally rich and very international society and moved back to Belfast in 2012 where I began to bring up my son as a single parent. We always read books together from when he was so tiny, and I wondered was it really that great to read from such a young age? But now at 7 years old, he is such an avid reader and communicator and I can see that it absolutely did. What I did notice was that there were so few characters in the books that looked like him. This baffled me and I wondered why this was. Of course, I could find the books when I looked for them, but they weren’t so readily available as they are now. Why is this representation so important though I hear you ponder …?
Well. The whole world is not white, able bodied and with a nuclear family structure. When children read books and don’t see people like them in them, they don’t feel included in society which can have a massive effect on their own confidence and self-worth. However, when there are characters similar to themselves culturally or ethnically, I have seen it reinforce a more positive view on themselves and pushes them towards goals and allows them to believe that anything is possible! How can you be what you can’t see, right?
Seeing characters, ideas and experiences in books that are unlike ours allows our children to open their minds and teaches them (and us for that matter) to value the whole human race and not just people who look like us. This equity within literature teaches empathy from a young age which helps them build secure and strong relationships with those around them while promoting tolerance and acceptance.
Being included in books and seeing other people like them facing challenges and making a difference in the world really helps kids have a deeper understanding of our world and how great things are possible. It creates impact, allows them to have role models they may never have met who influence their actions and behaviour, help them to overcome challenges and push them to their full potential.
Books with a diverse and inclusive representation allow a mirror or a window for what our next generation can do for themselves. They read about a wide range of human experience – familiar or strange, real or imagined and they can manifest a larger window of opportunity for themselves. This allows for authentic connections which allows them to feel less alone, more important and increases self-esteem.
While embracing books within education that promote diversity, equity and inclusion it is also important to encourage our kids to see colour, culture, history, identity and acknowledge the impact it has on our lives and experiences. Encouraging an actively diverse life through books, TV, films, toys, food music and embracing curiosity, welcoming questions and having the conversations can really encourage the next generation to have a clear understanding and acceptance that every human deserves to be treated fairly and with respect no matter who they are. And imagine the possibilities in a world like that.
We Need Diverse Books

Written by Anna Szpakowska
Professional Development Lead at Lyfta
The outpouring of shock, disgust and despair surrounding the murder of George Floyd this year rightly drew our attention to the discrimination suffered by so many on a daily basis. It also drew our attention to the institutional racism pervasive in much of our society. This heightened social awareness led to discussions of diversity in education, with calls for the history curriculum to include black British history and many English teachers sharing their recommended diverse reading lists or schemes of work online. In fact, some young people started a petition to ask the government to include The Good Immigrant and Why I’m No Longer Talking to White People About Race on the GCSE English Literature specification.
It was heartening to see so many educators impassioned to provide an education to young people which directly tackled issues of discrimination; it’s wonderful to work for a profession that not only wants to provide young people with knowledge and skills but also wants to make the world a better and more just place.
This is not the first time something like this has happened. In fact, in 2019, Edexcel were forced to add more texts from black, Asian and other minority ethnic writers to their GCSE Literature specification, after complaints about there being ‘too many dead white men’ on the reading list. This decision whilst perhaps well-intentioned, was met with disappointment from educators suggesting that the choices of texts, added by Edexcel, were not challenging enough. And, as Diane Leedham pointed out ‘As with all the exam boards in 2014, it’s clear that the people choosing the set texts that they frame as ‘diverse’ don’t have much knowledge of diaspora literature’.
Nevertheless, according to statistics from 2019, only 12.6% of students sitting an English Literature GCSE in 2019, sat the Edexcel qualification. In fact, the largest percentage (85%) of pupils sitting an English Literature GCSE in 2019 sat the AQA qualification. And figures from the AQA Examiner’s Report in 2019 show that of the most popular texts studied by all centres completing the AQA English Literature GCSE, all of the authors were white men, very few of the characters were women and none of the characters were black or Asian. The dilemma for educators then, is not only are the exam boards not providing enough suitable texts to truly reflect the experiences of most of us in society, but that the majority of schools themselves continue to choose to teach texts written by dead white men.
As teachers of English literature, we are the gatekeepers of books and literature accessed by many young people. It is, therefore, our moral obligation to expose young people to a wide variety of texts that provide them with a range of experiences, voices and characters. As Botelho and Rudman explain (expanding on Sims-Bishop’s metaphor of windows, mirrors and doors):
‘Children need to see themselves reflected so as to affirm who they and their communities are. They also require windows through which they may view a variety of differences…. Literature can become a conduit- a door- to engage in social practices that function for social justice’
Where are all the women?
For the purposes of this post, I will focus my thoughts on female writers, characters and issues of sexism and misogyny. That is not to say that I place more value on the inclusion of female writers and characters than I do on black authors and characters, gay authors and characters or authors and characters with disabilities, for example. I just feel that as a woman, I am best placed to discuss the issue of women in literature.
So, why then, in 2020, do we have to have a discussion about young people accessing texts written by and about women? And, why is it so important anyway? Aren’t women equal after all? Unfortunately, the answer is a resounding no. Despite the equal pay act being introduced fifty years ago this year, the UK’s gender pay gap is still 17.3% with the World Economic Forum reporting that it will take 202 years to close this gap. As well as this, statistics gathered from 2019, show that the number of women and girls murdered in 2019 rose by 10% on the previous year, to take it to the highest figure since 2006. It’s clear there’s much more work to be done before we can claim our equality.
With no shortage of female authors writing about the female experience, why do we continue to choose to teach texts written by and about men? The myth of the superiority of the ‘great’ English literary canon has a lot to answer for but what worries me a great deal is that teachers continue to buy into this myth. By continuing to teach these texts – and more often than not, attempting to mirror the GCSE curriculum at Key Stage 3 too – we perpetuate the notion that one voice (the white male) is superior to everyone else’s.
And, yes, it’s true that children may be reading plenty of texts by women and about women in their own time. But, when they haven’t been taught the critical skills to unpick the sometimes-sexist depiction of female characters, I fear that we are at risk of inculcating a generation of young people with sexist ideals.
Both young women and young men need to see a variety of female characters. They need to be able to discuss issues of sexism. It’s not our job to police what they read and discourage them from reading books such Louise Rennison’s Angus Thongs and Full Frontal Snogging because, as Kimberley Reynolds explains it depicts female characters who are ‘only interested in friends, fashion and fun’. But it is our job to show young people alternatives and teach them to read critically. Characters like Starr in Angie Thomas’ The Hate U Give, for example show a passionate, intelligent, strong and socially responsible young woman. Or, Dana in Octavia Butler’s Kindred could provide opportunity for discussions of gender and race whilst also providing them with an insight into the Antebellum South and the science fiction genre too. For teenagers (some of whom will already be sexually active), it’s important to address the issue of sexual assault. Books like Amber Smith’s The Way I Used to Be could be helpful in achieving this.
What’s key here is that teachers clearly have the passion, the willingness and the desire to teach a wider variety of authors and texts. I hope the passion and impetus we have garnered this year does not disappear and our calls for a more diverse reading list can be implemented. But what must also accompany these reading lists and all literacy education is critical discussions about how and why characters are presented in certain ways.
Diversity and inclusion - why are they not easy bedfellows?

Written by Amanda Gummer
20 years experience working with children and families
Two very hot topics at the moment but the approaches to increase diversity and improve inclusion can seem to conflict with each other, preventing either of them from being fully achieved. In order to achieve true diversity and inclusion we need to rethink some of the accepted wisdom.
When we talk about inclusion, we are often referring to disabilities and making sure children with additional needs are able to access the play or developmental opportunities that other children can. Similarly, when we talk about diversity, we’re usually talking about race, and occasionally gender. However, to truly be inclusive and diverse, we need to look outside of physical, and even mental conditions, and consider factors such as culture, geography, socio-economic status, and age. Only then can we achieve full inclusion and by breaking down those barriers we will automatically increase diversity. First, it is helpful to look at the evolution in our approach to inclusion. The same diagram can be used for diversity.
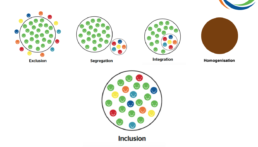
However, not everyone is on the same journey or going at the same speed on this. For example, many playgrounds were commissioned decades ago when the concept of inclusion wasn’t a priority – at best, there was a single, wheel-chair accessible piece of equipment – very little consideration was given to other disabilities and conditions which impact a child’s ability to play.
The toy industry has been stuck using the segregation approach for years – toys designed for children with additional needs are not readily available in mass-market toy shops or supermarkets and so are not able to benefit from the economies of scale of the most popular toy brands and are therefore more expensive and seen as very niche.
Clearly segregation is where the diversity movement started. Integration wasn’t much better for increasing racial tolerance and appreciating individual differences, but I think that the biggest backwards step was when, possibly with the best of intentions, we moved towards homogenisation. The principle being that if not everyone could have something, no one should. So everything became bland – we introduced a national curriculum which meant that children in a vibrant inner city school couldn’t make the most of the opportunities in their community because the kids in the rural village school didn’t have the same access, and children living in the countryside with access to lots of space and natural resources were not able to make the most of that in their education because it wasn’t accessible to the kids in the inner cities. Examples of this one-size-fits-all approach can be seen in lots of walks of life – from the rise in chain stores and the loss of individual towns’ personalities, to pre-packaging of food, fast fashion – the list goes on.
The result? An education system that is inflexible with very narrow definitions of success, playgrounds that are vandalised and misused because they’re not inclusive enough (not enough children are using them for them to be seen as a community asset and protected by the people in those communities), High Fat Salt and Sugar packaged foods, and a loss of character on our high streets. This all contributes to a lack of understanding and appreciation of individual differences and differing needs. And it is time for that to change.
I’m focussing on toys and play as that’s what I know but I’m fairly certain this is relevant in a lot of other arenas. We need to take some bold steps and recognise that true inclusion comes from appreciating children’s differences – and this naturally leads to more diversity. By considering all of the potential barriers to inclusion and working to remove them we are automatically increasing diversity. A playground that includes challenging risky play will not only appeal to children with ADHD but will also be used by older children and maybe those who can’t afford to go to the theme parks but crave a bit of an adrenaline rush. Understanding the dress codes of different cultures allows equipment to be included that doesn’t require climbing or leg lifting and is accessible to children in those clothes, as well as children on crutches.
So what’s to be done. Well first of all we need to get rid of the tokenism or ‘inclusion theatre’ all the things that look good and seem like they are promoting inclusion but are not based on any evidence and in the worst cases may actually be impeding inclusivity. To be truly inclusive and increase diversity, we need to take an evidence-based approach and include consultation with all stakeholders – whether that’s in town planning, toy design, playground procurement or shop layouts.
We also need to realise that a single product/brand/service can’t be all things to all people but should be accessible and relatable to by the people it’s designed for. A toy can not be multisensory and stimulating whilst also being quiet and relaxing. The important thing is to make sure that everyone’s needs are respected and catered for overall.
It’s really not rocket science but we need to update our approaches to both inclusion and diversity if we’re ever to really achieve either.
Amanda is a research psychologist and founder of the Good Play Guide: www.goodplayguide.com
Why Diversity Matters in Education: “The rise of an internationally-minded child.”

Written by Fatma Khalid
A lot has been written recently about diversity, especially in education. Whilst diversity has been “entertained” by a lot of administrators and specifically policy makers into bringing the novelty idea to practice, there is still a lot to be done in terms of making our society and specifically our educational sector more diverse.
Majority of times I have seen students, even my own children, being confused about their culture and identity specifically for children who are born and raised in countries that are not their countries of origin. The implications of this reaches out to sometimes loss of identity or even worse the breed of inferiority that we find most common even here in the UAE where certain cultures and nationalities are often viewed as being better because of how they are portrayed or advocated. This is further challenged by the market niche in the UAE which gravitates towards recruiting teachers of certain nationalities further compromising the practice or need for diversity and inclusivity. Children grow up feeling that the most knowledgeable and people holding high offices are isolated to only ‘a certain kind’ which itself is a huge impediment to ambition and self-esteem.
Although schools have tried to review their curriculums to include enriched activities that promote culturally diversified programs, little has been done to support world-wide inclusiveness or build a truly “international minded” child. Curriculums majority of times are still country bound; where they cover history or cultures to that particular country as compared to covering world history and include studying cultures of the world so children can truly build acceptance and respect and be aware of other cultures that are unique and significantly different to theirs; this is what after all is defined as an “international minded child”. How else can a child build compassion or become a global citizen if he/she spends all their lives thinking there was only one culture or history that was worth studying and understanding.
All efforts need to be in place to ensure that all children’s cultures are represented in curriculum which is highly recommended for a highly inclusive society such as the one here in the UAE. Culture awareness cannot be left for isolated occasions such as the most commonly celebrated “international day” where children and parents are encouraged to bring their traditional food and dress in their traditional clothes, then tribute done and the rest of the year, children go back to studying the curriculum (country bound) history. When we have made technology a mandate, cultural diversity too holds importance and should be integral and be embedded in our core curriculums.
Moreover, ensuring that our teams are made up of qualified individuals from different nationalities increases the opportunity for children to learn and understand cultures from multiple countries that most importantly also represents them. Curriculums are consequently enriched with creativity and increased global perspective for a truly diverse society that aims to understand, acknowledge and accept that although we are different, we are fundamentally the same kind…
The human kind.

